Fix 403 Forbidden Error on wp-admin in WordPress
What is the 403 Forbidden Error on wp-admin?
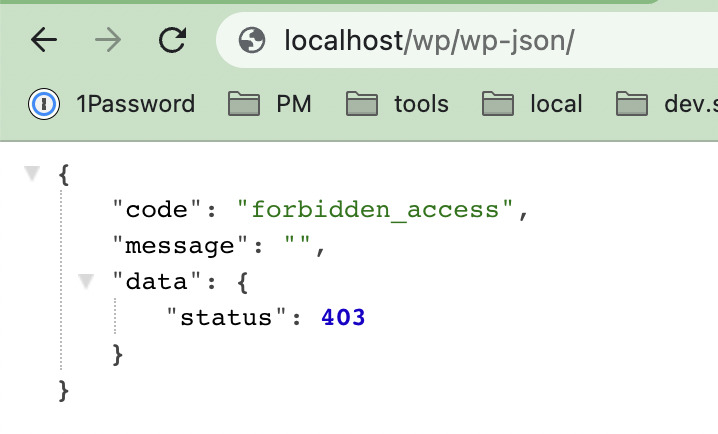
The 403 Forbidden Error on wp-admin is a common WordPress issue where users are denied access to the admin dashboard. It typically appears with a message like:
403 Forbidden – You don’t have permission to access /wp-admin/ on this server.Code language: JavaScript (javascript)This error prevents access to:
- wp-admin
- wp-login.php
- Dashboard functionalities
- Theme and plugin settings
Common Causes of 403 Forbidden Error on wp-admin
A 403 Forbidden error on the WordPress /wp-admin page signals that the server is actively denying access to the admin dashboard. Unlike 404 errors (not found), a 403 error means that the resource exists, but your request is blocked. Understanding the root causes is critical to diagnosing and fixing the issue efficiently.
Below are the most common technical reasons, with logic, explanation, and technical context:
Corrupted or Misconfigured .htaccess File
The .htaccess file is a critical Apache configuration file used for rewriting URLs, setting access permissions, and controlling security policies.
If your .htaccess file contains:
- Incorrect Deny from all rules
- Overly strict RewriteCond directives
- Syntax errors
…it can inadvertently block access to the /wp-admin directory.
Example of a bad rule:
<Directory /wp-admin>
Deny from all
</Directory>Code language: HTML, XML (xml)This would prevent anyone, including you, from accessing the admin dashboard.
Even a missing RewriteBase / or malformed cache rule can lead to 403 errors.
Incorrect File and Folder Permissions (403 Due to Permission Denied)
Web servers require specific file and folder permission settings to allow legitimate access. Incorrect permissions can make files or directories inaccessible, leading to a 403 error.
Recommended permission settings:
- Folders (including /wp-admin/): 755
- Files (like index.php, wp-config.php): 644
Example of problematic settings:
- Files set to 000, 400, or 600 (server sees them as inaccessible)
- Ownership set to a different user (e.g., migrated site where files are owned by a different server account)
You can check and modify permissions via FTP or SSH using chmod.
ModSecurity (WAF) Blocking wp-admin Requests
ModSecurity is a popular Web Application Firewall (WAF) used by many hosting providers. It scans incoming HTTP requests for malicious patterns.
However, certain legitimate requests to /wp-admin/—especially AJAX calls, query strings, or custom admin URLs—might trigger false positives.
Common ModSecurity issues:
- Admin-ajax requests getting blocked
- Certain plugin actions (e.g., backup, security scan) marked as suspicious
- Forbidden POST requests while saving settings
If ModSecurity logs show 403 responses for your IP or specific rule IDs (e.g., 340003), you’ll need to contact your host to whitelist or disable the triggered rules temporarily.
WordPress Security Plugins Blocking Admin Access
Many popular WordPress security plugins allow you to block access to /wp-admin/ based on certain rules.
Plugins that commonly cause this:
- Wordfence
- iThemes Security
- All-in-One WP Security & Firewall
If you’ve enabled features like:
- Hide or rename login page
- Country/IP-based restrictions
- Brute-force protection after X failed logins
- CAPTCHA blocking
…it may result in the 403 error, especially after plugin updates or server migrations.
In many cases, the plugin logs will show the reason for the denial.
IP Deny Rules in .htaccess, wp-config.php, or Server Configuration
Sometimes, admins manually block suspicious IPs using .htaccess rules or the server’s firewall (e.g., NGINX or UFW).
However, misconfigurations or over-aggressive plugins can accidentally block your own IP or admin IPs.
Sample .htaccess block:
<Limit GET POST>
order allow,deny
deny from 192.168.1.50
allow from all
</Limit>Code language: HTML, XML (xml)This will deny access to anyone from the specified IP, including admin users if misapplied.
Corrupted WordPress Core Files or Incomplete Site Migration
A failed update or improperly handled site migration can result in missing or corrupted core WordPress files. Critical files such as:
- wp-login.php
- files in /wp-includes/
- files in /wp-admin/
…may be lost or modified, causing the system to return a 403 error during login or dashboard access.
You should compare your installation with a clean WordPress version or restore from a working backup.
Restrictive Server Configuration (e.g., NGINX Rules)
On servers using NGINX instead of Apache, configuration files like nginx.conf or virtual host settings might contain directives that block admin paths.
Example NGINX restriction:
location ~* /wp-admin/ {
deny all;
}Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Such rules are often inserted for performance or security purposes but can easily misfire in multi-user environments.
CDN or Proxy Interference (e.g., Cloudflare Rules)
If your site is behind a CDN like Cloudflare, 403 errors can originate from:
- WAF rules blocking admin URLs
- Misconfigured page rules or caching
- Rate limiting features blocking your IP
Always verify the CDN’s firewall logs or pause Cloudflare temporarily for debugging.
Hosting-Level Firewall or Restrictions
Some hosting providers (especially shared or managed WordPress hosting) impose additional firewall layers or malware scanning engines. These can block access to /wp-admin/ if suspicious activity is detected.
This is common with providers like:
- Bluehost
- SiteGround
- HostGator
In such cases, contacting hosting support is often required to whitelist the request.
Malware or Hacked Redirects
Infected WordPress installations may have malicious .htaccess rules, injected code, or backdoors that restrict access to the admin area or redirect it elsewhere.
Check for:
- Suspicious .htaccess content
- Unknown plugins or themes
- Base64 or eval obfuscated code in PHP files
Malware scanners such as Wordfence, Sucuri, or MalCare can help identify such issues.
Step-by-Step: How to Fix 403 Forbidden Error on wp-admin
Backup Your Site Before Making Any Fixes
Always back up your full WordPress site (files + database) using plugins like UpdraftPlus, or your hosting cPanel.
Fix Corrupted .htaccess File
Step 1: Access and Rename .htaccess
- Login to your server via FTP or File Manager.
- Navigate to /public_html/ or root directory.
- Find .htaccess and rename it to .htaccess_backup.
Step 2: Generate a New Default .htaccess File
Go to your dashboard (if accessible) → Settings → Permalinks → Save Changes.
If you can’t access wp-admin, manually create a new .htaccess file:
# BEGIN WordPress
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c>
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteRule ^index\.php$ - [L]
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule . /index.php [L]
</IfModule>
# END WordPressCode language: HTML, XML (xml)Save it as .htaccess in the root directory.
Reset File and Folder Permissions
Use cPanel or SSH to Reset Permissions
Correct permissions:
- Files: 644
- Folders: 755
Using SSH:
find /home/username/public_html/ -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;
find /home/username/public_html/ -type f -exec chmod 644 {} \;Change Ownership (Advanced)
If files were uploaded by different users or scripts:
chown -R username:username /home/username/public_html/(Replace username with your hosting account name)
Disable ModSecurity in cPanel
- Login to cPanel.
- Go to ModSecurity.
- Select your domain.
- Click Disable next to it.
Contact hosting support if you cannot find ModSecurity settings.
Deactivate All Security Plugins via FTP
Step 1: Go to /wp-content/plugins/
Step 2: Rename folders of security plugins:
- wordfence → wordfence_backup
- ithemes-security → ithemes-security_backup
This disables them temporarily. Now try logging into /wp-admin/.
Check .htaccess for IP Block or Deny Rules
Open .htaccess and look for lines like:
deny from 192.168.1.1Code language: CSS (css)Comment out or remove any deny from or Require all denied lines blocking access.
Whitelist Your IP (Optional)
If you’re using an IP whitelist plugin or firewall (like Cloudflare or CSF), make sure your IP is whitelisted.
Check Hosting Firewall or Malware Scanner
Some hosts automatically block access to wp-admin if:
- Malware is detected.
- Too many failed logins occur.
Contact your host and request a security scan or temporary unblocking.
Restore Core WordPress Files
Download the latest WordPress package from wordpress.org.
Upload and overwrite these folders (except wp-content):
- /wp-admin/
- /wp-includes/
Avoid uploading wp-content to prevent data loss.
Check wp-login.php Integrity
Sometimes wp-login.php is corrupted or deleted.
Reupload wp-login.php from a fresh WordPress ZIP package.
Fixing 403 Forbidden After WordPress Migration
If this error happens after site migration:
- Double-check .htaccess, file permissions.
- Regenerate permalinks.
- Clear any hardcoded URLs in plugins or themes.
- Search database for old domain entries using tools like Better Search Replace.
Conclusion: Regain Access to Your WordPress Dashboard
The 403 Forbidden Error on wp-admin can seem intimidating, but it’s usually fixable by checking:
- .htaccess
- File permissions
- ModSecurity
- Plugins
- Hosting rules
By systematically applying the fixes in this guide, you can restore full access to your WordPress dashboard without downtime.