Fix Crawled – Currently Not Indexed in Google Search Console
What Does “Crawled – Currently Not Indexed” Mean?
Fix Crawled – Currently Not Indexed is a common issue many website owners face in Google Search Console. It means that Googlebot has crawled your page, but it hasn’t added it to the index—so it won’t appear in search results. This problem can seriously affect your SEO performance, especially if it affects important pages on your site.
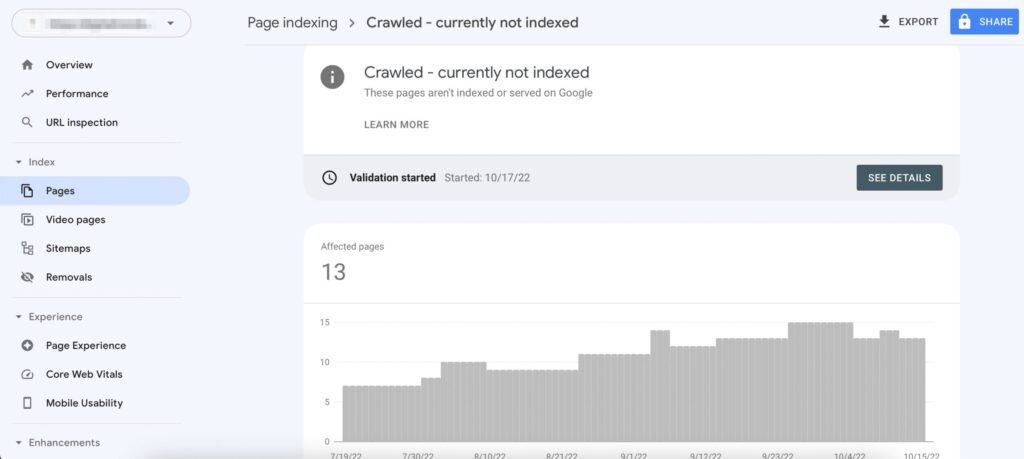
In this guide, you’ll learn how to diagnose and fix “Crawled – Currently Not Indexed” issues with proven solutions for WordPress, Shopify, custom websites, and more. Whether you’re an SEO manager, developer, or content strategist, this article offers technical and practical fixes to get your pages indexed.
Difference Between “Crawled – Currently Not Indexed” vs “Discovered – Currently Not Indexed”
- Crawled – Currently Not Indexed: Googlebot accessed the page but didn’t index it.
- Discovered – Currently Not Indexed: Google knows the URL exists but hasn’t crawled it yet.
Understanding the difference helps in identifying where in the indexing pipeline your problem lies.
Why Is Your Page Crawled but Not Indexed?
There are several potential causes:
Low Content Quality
Google’s index is built to serve high-quality, useful content. If your page doesn’t meet its standards, it may get crawled but skipped.
- Thin content: Pages with too little useful text, often under 300–500 words, provide minimal value.
- Duplicate or near-duplicate: Pages that are too similar to others on your site (or elsewhere) may be ignored to avoid index bloat.
- Auto-generated or AI-spun content: Content that lacks coherence, context, or uniqueness can be flagged as low quality.
- No unique value: Even if the content is “original,” Google may skip it if it doesn’t offer anything new or helpful compared to existing indexed pages.
Crawl Budget Limitations (Especially for Large Sites)
For large or frequently updated sites, Google sets a “crawl budget” — a limit to how many URLs it will crawl within a timeframe.
- If your sitemap or internal linking prioritizes less important pages, valuable URLs might not get crawled efficiently.
- URLs may be crawled once but not indexed if Google determines them to be low-priority or redundant based on early analysis.
Poor Internal Linking Structure
Pages that are deeply nested in your site structure or lack sufficient internal links may be seen as “unimportant” by Googlebot.
- Orphaned pages (no internal links pointing to them) are rarely indexed.
- URLs several clicks away from the homepage often have lower crawl priority.
Conflicting Canonical or Meta Signals
If your page sends mixed indexing signals, Google might skip it to avoid confusion.
- Incorrect canonical tags: Pointing to another page or self-canonicalizing incorrectly can lead Google to skip the page.
- Inconsistent metadata: Title, description, and hreflang attributes that don’t align with page content can reduce trust.
- Alternate hreflang conflicts: Misconfigured multilingual setups can cause pages to be misinterpreted or skipped.
Noindex or Robots.txt Issues (Current or Legacy)
Even if a page is now indexable, Google’s historical signals may delay re-evaluation:
- A URL that was previously disallowed in robots.txt or marked noindex may remain excluded for days or weeks after being fixed.
- Google doesn’t re-crawl pages constantly — some URLs are reprocessed slowly, especially on low-authority sites.
Indexing Delay for New Websites or Pages
Google treats newly launched websites and pages with caution.
- If your domain has no prior trust signals, indexing may be delayed regardless of content quality.
- Pages without backlinks or internal references are even more likely to be skipped at first.
How to Fix “Crawled – Currently Not Indexed”
Improve Content Quality
- Ensure the page is original, informative, and comprehensive.
- Use proper structure: headings, paragraphs, lists, media.
- Avoid duplicate or auto-generated content.
Strengthen Internal Linking
- Link to the unindexed page from other high-authority pages on your site.
- Add the page to your main navigation, footer, or sitemap.
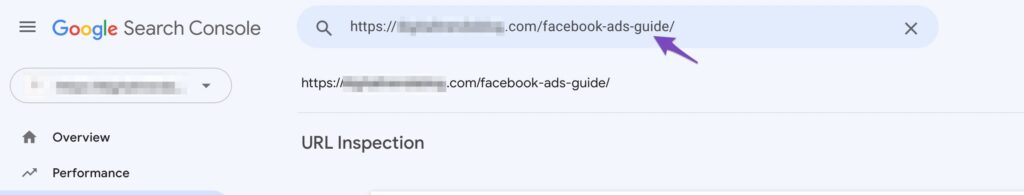
Resubmit via URL Inspection Tool
- Go to GSC > URL Inspection > Enter URL > Request Indexing
- Make sure the page returns HTTP 200 and is mobile-friendly.
Check for Canonical or Meta Tag Conflicts
- Remove unnecessary canonical tags that point elsewhere.
- Ensure the page is not marked noindex accidentally.
Add External Backlinks
- Get at least 1–2 links from other indexed domains pointing to the page.
- This increases the page’s importance in Google’s eyes.
Monitor Index Coverage Reports
- Keep an eye on the GSC Index Coverage to check if the page moves to “Indexed”.
- If it returns to “Crawled – Currently Not Indexed,” reassess the content and linking.
Validation Failed vs Passed in GSC
- Validation Failed: Your fix was tested by Google, but the page still had the same issue.
- Validation Passed: Google confirmed the issue is resolved, and the URL should now be eligible for indexing.
Use the “Validate Fix” button only after ensuring all technical and content issues are resolved.
Special Cases: WordPress, Shopify, Reddit Pages
WordPress: Troubleshooting “Crawled – Currently Not Indexed”
WordPress sites often suffer from indexing issues due to plugin conflicts or incorrect settings. Here’s how to investigate:
Check Noindex Tags with SEO Plugins
Go to your SEO plugin settings (e.g., Yoast SEO or Rank Math). Open the post/page settings and ensure “noindex” is not enabled for the page. Many times, users accidentally set noindex for important content during publishing or template editing.
Review Your Sitemap and Page Inclusion
Navigate to your XML sitemap (e.g., /sitemap_index.xml). Confirm that the affected page is listed there. If it’s missing, ensure the page is published, not excluded manually, and not set to private.
Investigate Theme or Plugin Conflicts
Some plugins (especially security, caching, or custom post types) may unintentionally add headers or meta tags that block indexing. Disable suspicious plugins temporarily and check if the page becomes indexable via site:yourdomain.com/page-url.
Improve Content Signals
WordPress-generated pages can often be thin or templated (e.g., tag pages, archives). Make sure the affected page includes unique, valuable content beyond auto-generated layouts.
Review Robots.txt and .htaccess
Access the file via FTP or File Manager in your hosting panel. Ensure your /robots.txt doesn’t block paths like /wp-content/, /wp-includes/, or the page URL itself. Also, scan .htaccess for any unexpected Disallow or redirection rules.
Shopify: Common Reasons for Pages Not Being Indexed
Shopify platforms, while SEO-friendly, can encounter indexation issues due to duplicate templates or improper setup:
Avoid Template Duplication
Shopify creates multiple URL variations for products via collections (e.g., /collections/shirts/products/red-shirt vs /products/red-shirt). Use canonical tags to point to the main product URL and avoid duplicate content dilution.
Theme Code and Robots.txt.liquid
Open the theme.liquid or robots.txt.liquid files in your theme editor. Ensure no unnecessary Disallow rules are present that block important collections or product URLs. For instance:
Disallow: /collections/*+* ← can block filtered collection pagesCode language: JavaScript (javascript)Check for Pagination/Filter Trap
Shopify’s filter or sort features can create near-duplicate pages (e.g., ?sort_by=best-selling). Ensure you’re using canonical tags and parameter rules in Google Search Console to consolidate index signals.
Avoid Content Automation
Do not rely on auto-generated product descriptions or duplicated manufacturer content. Use unique and keyword-optimized copy.
App Conflicts
Certain apps (like translation or review plugins) can add hidden elements or conflicting meta directives. Test by disabling recently added apps and rechecking the page headers.
Reddit, Forums, or User-Generated Content (UGC): Why It’s Not Indexed
Platforms like Reddit or your own forum-based site often struggle with indexing UGC due to perceived low value:
Thin, Low-Engagement Pages
Google avoids indexing short posts or threads with no comments, votes, or engagement. Prioritize indexing content that gets traction, backlinks, or dwell time.
Duplicate Questions/Answers
Forums often have repeated questions or responses. Google will index only one version if it deems the rest redundant.
External or Affiliate-Only Pages
If your UGC page exists solely to link out (e.g., to affiliate content or Reddit discussions), Google may ignore it unless it’s wrapped in unique commentary or editorial input.
Improve Discoverability and Authority
Add internal links from strong pages (homepage, blog posts) to the UGC page. Submit via Google Search Console using the “Inspect URL” tool after enriching the content.
Indexing Settings for UGC Platforms
Ensure your UGC platform allows indexing of dynamic URLs. Some forum systems or SPA frameworks require extra configuration like server-side rendering (SSR) or pre-rendering for crawlers.
How to Force Google to Index a Page
While you can’t “force” Google, you can:
- Use GSC’s URL Inspection > Request Indexing
- Add strong internal/external links
- Ensure technical readiness (200 OK, canonical, sitemap, mobile)
- Use Schema Markup to enhance visibility
Frequently Asked Questions
Why are some URLs stuck in “Crawled – Currently Not Indexed” for months?
Thin or duplicate content: If the page lacks original, valuable content, Google may choose not to index it.
Lack of internal or external links: Pages with poor link signals are considered low-priority for indexing.
Low crawl budget: For large sites, Google prioritizes certain sections over others. Less important pages may get crawled but not indexed.
Slow-loading or blocked resources: If the page can’t fully render due to JavaScript issues or blocked assets, indexing may be skipped.
Noindex history: If the URL previously had a noindex directive, Google might delay re-evaluation even after the tag is removed.
Can pages stay in this status forever?
Yes, a page can stay in “Crawled – Currently Not Indexed” permanently if it continues to be seen as low quality or irrelevant to search intent. Google doesn’t guarantee indexing for every page it crawls. If your content doesn’t offer new, useful, or unique value to users, Google may never add it to the index—regardless of how often it’s crawled.
To avoid this, focus on content quality, topical relevance, and internal linking. Sometimes a full rewrite or change in page purpose is necessary.
Is this a penalty?
No, this is not a Google penalty. It’s simply Google making a decision not to index your content yet. Unlike penalties (which usually result from violating Google’s Webmaster Guidelines), this issue is more of a filtering decision. Googlebot may crawl the page, but based on signals such as content depth, structure, or site authority, the algorithm may determine the page doesn’t meet the current quality threshold.
In many cases, you can fix this status by improving content, making sure it’s internally linked, submitting it via Google Search Console, and ensuring technical SEO is clean.
Conclusion
Fixing the “Crawled – Currently Not Indexed” issue isn’t about quick hacks — it’s about aligning your website with what Google expects from high-quality, index-worthy content.
To resolve this status, you need to address three core pillars:
- Technical foundation: Ensure your site is crawlable, fast, and free from index-blocking directives or rendering issues.
- Content quality: Create original, helpful, and unique content that serves clear intent and adds real value to users.
- Crawl signals: Strengthen internal linking, acquire relevant backlinks, and prioritize important URLs in your site architecture and sitemaps.
Understanding why Googlebot crawls but doesn’t index your pages is key to solving the problem. When your site meets both technical and content expectations, indexing will follow — and so will visibility in search results.