Fix Robots.txt Blocking Googlebot: Full SEO Guide
When your website’s visibility in Google Search drops or pages fail to get indexed, one critical factor to check is your robots.txt file. Improperly configured robots.txt rules can block Googlebot from crawling essential content. This guide will walk through how to fix robots.txt blocking Googlebot, with specific insights for WordPress, Shopify, Squarespace, and broader SEO implications.

What is robots.txt and How It Affects Googlebot Crawling
Overview of robots.txt File
The robots.txt file is a plain text file located in the root directory of your website (e.g., https://example.com/robots.txt). It instructs search engine crawlers (also known as user-agents) which parts of the website they are allowed or not allowed to access.
Role of robots.txt in SEO and Googlebot Access
For SEO purposes, robots.txt helps manage crawl budget, protect sensitive pages from being crawled, and avoid indexing duplicate or irrelevant content. However, if misconfigured, it can prevent Googlebot from accessing critical areas like CSS, JavaScript, images, sitemaps, or entire directories, resulting in poor indexation and rendering issues.
How to Detect If Googlebot Is Blocked by robots.txt
Check Google Search Console
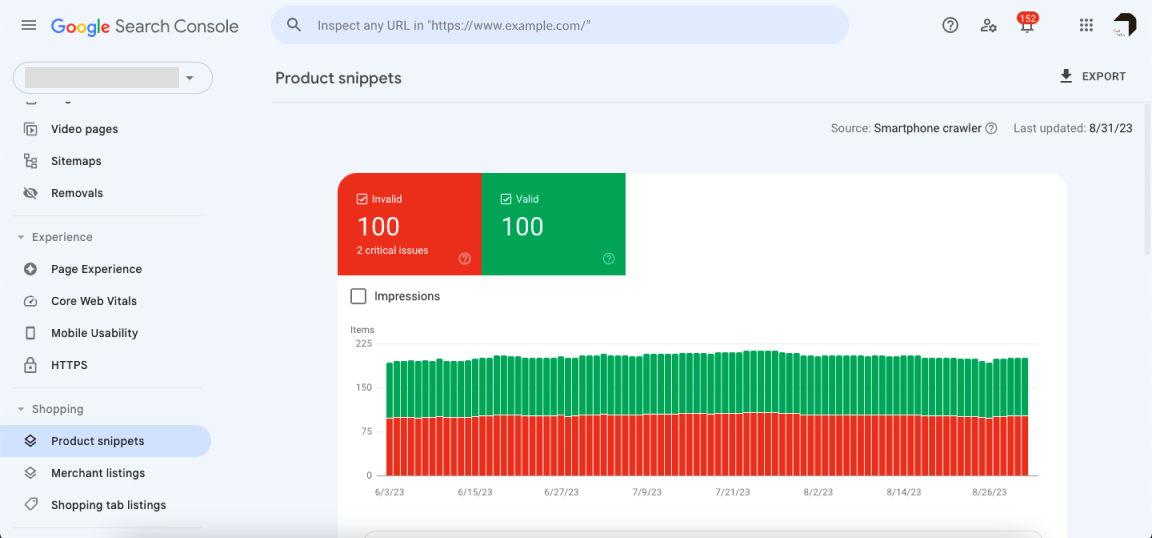
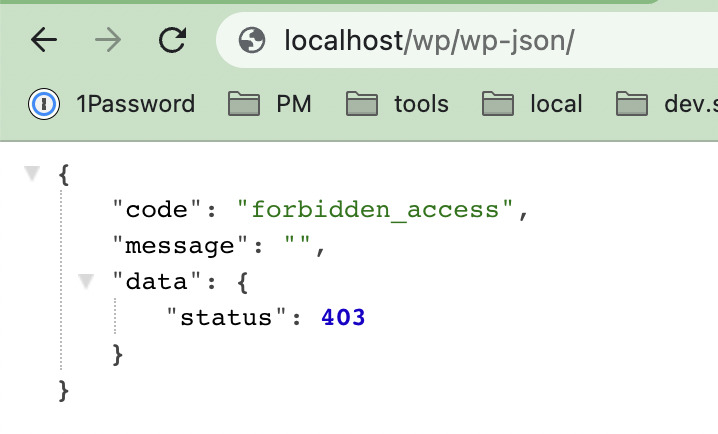
In Google Search Console, go to Pages > Crawled – currently not indexed. Look for pages with the message “Blocked by robots.txt.” This indicates that Googlebot attempted to crawl the page but was denied by a rule in your robots.txt file.
You can also inspect individual URLs using the URL Inspection Tool. Check the Crawl section to see if it says “Crawling allowed? No: blocked by robots.txt.”
Use robots.txt Tester Tool
Google offers a dedicated robots.txt Tester: https://www.google.com/webmasters/tools/robots-testing-tool
This tool lets you input any URL on your site and simulate how Googlebot interprets your robots.txt file. It highlights the specific rule causing the block.
Look for Indexing and Render Issues
If Googlebot can’t crawl your CSS, JS, or image files due to a robots.txt block, your pages may render improperly in search results. This can harm mobile usability, Core Web Vitals, and overall SEO.

Common Robots.txt Mistakes That Block Googlebot
Disallowing Everything by Mistake
A common error is unintentionally blocking all crawlers from your entire site:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /Code language: HTTP (http)This tells all bots, including Googlebot, not to crawl any pages.
Blocking Essential Directories (wp-content, assets)
Disallowing directories like /wp-content/, /js/, or /images/ can prevent Googlebot from accessing stylesheets, scripts, and media files, which are essential for proper page rendering.
Incorrect Wildcards or Syntax
Improper use of * and $ in robots.txt can cause over-blocking. For example:
Disallow: /*.php$Code language: HTTP (http)This rule blocks all URLs ending in .php, which may include key pages like index.php or product.php.
Blocking Sitemap or Admin Paths Improperly
Some mistakenly block sitemap URLs:
Disallow: /sitemap.xmlCode language: HTTP (http)Others block WordPress admin without allowing AJAX:
Disallow: /wp-admin/Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Others block WordPress admin without allowing AJAX:
Disallow: /wp-admin/
You should allow AJAX scripts:
Allow: /wp-admin/admin-ajax.phpCode language: JavaScript (javascript)How to Fix Robots.txt Blocking Googlebot
Edit the robots.txt File Properly
Access your robots.txt file via your file manager, FTP, cPanel, or CMS plugin. The goal is to allow Googlebot full access unless there’s a specific reason to restrict it.
Recommended baseline configuration:
User-agent: Googlebot
Disallow:
User-agent: *
Disallow:
Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap.xmlCode language: JavaScript (javascript)Allow CSS, JS, and Image Files
Ensure directories containing styles, scripts, and images are not blocked. If you use WordPress, Shopify, or Squarespace, do not disallow /wp-content/, /assets/, /static/, or /media/.
Test with the Mobile-Friendly Test or URL Inspection Tool to ensure full render access.
Specific Fixes for WordPress
Use plugins like Yoast SEO to edit robots.txt directly. Make sure essential resources aren’t blocked. Common fix:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /wp-admin/
Allow: /wp-admin/admin-ajax.phpCode language: HTTP (http)Avoid blocking /wp-content/, which holds themes, plugins, and media files.
Specific Fixes for Shopify
Shopify auto-generates robots.txt but allows customization. Use the theme code editor or an SEO app to override default blocks.
Ensure you don’t block /products/, /collections/, /blogs/, or sitemap URLs.
Specific Fixes for Squarespace
Squarespace generates robots.txt automatically and doesn’t support direct editing. However, avoid injecting noindex or disallow via code blocks that conflict with robots.txt. Contact support for escalated SEO issues.
Tools to Test, Validate, and Generate robots.txt
Robots.txt Validator
Use tools like Screaming Frog, Ryte, or Ahrefs to validate syntax and ensure rules behave as intended.
Robots.txt Tester Tool
Provided by Google, this lets you simulate how Googlebot interprets your file. Identify the specific rule blocking access.
Robots.txt Generator Online
Tools like Yoast, Small SEO Tools, and SEO SiteCheckup help generate a clean robots.txt file for beginners.
Robots.txt Viewer and Editor Tools
View and edit robots.txt directly from tools like Rank Math (WordPress) or built-in editors in some SEO dashboards.
Best Practices for Robots.txt Configuration
Allow Important Crawlers (Googlebot, Bingbot)
Always allow well-behaved crawlers unless you have a strong reason to restrict them.
Don’t Block Critical Resources
Avoid disallowing stylesheets, JavaScript, and images. These are critical for rendering and Core Web Vitals.
Use Disallow Judiciously
Only disallow sections like:
Disallow: /search/
Disallow: /?s=Code language: HTTP (http)These blocks reduce crawl of low-value pages.
Regularly Audit robots.txt
Run monthly audits via Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, or Sitebulb to catch accidental blocks.
How to Block Specific URLs in robots.txt
To block individual URLs:
Disallow: /private-page/
Disallow: /hidden-directory/Code language: JavaScript (javascript)To block URL patterns:
Disallow: /*.pdf$
Disallow: /*?ref=Code language: HTTP (http)Avoid using robots.txt for sensitive content—use authentication or noindex meta tags.
FAQs about Fixing robots.txt Blocking Googlebot
Why is Googlebot still not crawling my site after fixing robots.txt?
Check for noindex meta tags, poor internal linking, or crawl errors unrelated to robots.txt.
Should I disallow wp-admin in robots.txt?
Yes, but allow admin-ajax.php for front-end functionality.
What’s the difference between Disallow and Noindex?
Disallow stops crawling. Noindex prevents indexing. You can’t combine them effectively—Google can’t see the noindex if it’s disallowed.
Can I use wildcards in robots.txt?
Yes. Googlebot supports * and $. Use carefully to avoid over-blocking.
Conclusion
Your robots.txt file is a powerful tool to control crawler access, but with great power comes great responsibility. An overly restrictive configuration can cripple your SEO by blocking Googlebot from accessing important resources. Whether you’re running a WordPress blog, a Shopify store, or a Squarespace site, review and optimize your robots.txt regularly. Use Google’s tools to test, validate, and ensure your site remains crawlable and indexable.