The Complete Guide to Google Tag Manager (GTM) for Beginners and Advanced Users
What is Google Tag Manager and Why You Should Use It
Google Tag Manager (GTM) is a free tool by Google that allows you to manage and deploy marketing tags (snippets of code or tracking pixels) on your website or mobile app without modifying the codebase directly. It simplifies the process of adding tools like Google Analytics, Facebook Pixel, Hotjar, and conversion tracking, all in one central dashboard.

Without GTM, you’d have to manually insert code into your site’s HTML—a risky and time-consuming process. GTM eliminates this hassle, streamlining workflow, reducing errors, and empowering marketers to track performance independently.
Key Benefits of Using Google Tag Manager
- No developer dependency: Add or update tags without waiting on development cycles.
- Fast deployment: Launch new tags in minutes.
- Centralized control: Manage all tracking codes from one place.
- Debugging and version control: Built-in preview and versioning tools.
Step-by-Step: How to Set Up Google Tag Manager
Step 1: Create a Google Tag Manager Account
- Visit tagmanager.google.com
- Click Create Account, name your account (e.g., your company name)
- Enter your container name (usually your domain name)
- Choose “Web” as the platform and click Create
Step 2: Add GTM Code to Your Website
After account creation, GTM provides two code snippets:
- One placed immediately after the opening tag
- One placed immediately after the opening tag
Paste these into your site’s HTML or use your CMS’s integration (like via a plugin for WordPress).
Step 3: Verify Installation
Use the GTM Preview Mode or the Tag Assistant Chrome extension to confirm GTM is correctly installed.
Understanding the Core Components of Google Tag Manager
Tags
Tags are snippets of code used for tracking. Common examples include:
- Google Analytics (GA4)
- Google Ads Conversion Tracking
- Facebook Pixel
- Hotjar tracking code
Triggers
Triggers tell GTM when to fire a tag. Types include:
- Page View
- Click
- Form Submission
- Scroll Depth
- Custom Events
Variables
Variables hold dynamic data GTM uses in tags and triggers.
Examples:
- Built-in Variables (Page URL, Click Classes)
- Custom Variables (e.g., custom JavaScript)
Deploying Google Analytics 4 with GTM
- Create a new tag
- Choose Google Analytics: GA4 Configuration
- Enter your Measurement ID from GA4
- Set Trigger as All Pages
- Save and publish
You can also track custom events (like button clicks) using GA4 Event Tags.
Installing Facebook Pixel with GTM
- Go to Facebook Events Manager, copy your Pixel ID
- In GTM, create a new tag → Custom HTML
- Paste the base code from Facebook
- Add a trigger to fire on All Pages
- For event tracking (like purchases), create additional event tags
Scroll Tracking and Click Tracking with GTM
Scroll Tracking
- Enable built-in scroll variables
- Create a Scroll Depth trigger
- Set tag (e.g., GA4 event) to fire when user scrolls 25%, 50%, etc.
Click Tracking
- Enable Click Classes, Click ID variables
- Create a Click trigger for specific elements
- Fire a tag (e.g., GA4 event) on that trigger
Tracking Form Submissions and YouTube Video Views
Form Tracking
- Use built-in form variables
- Set a Form Submission trigger
- Fire a tag with the relevant event name
YouTube Video Tracking
- Use the YouTube Video trigger in GTM
- Track Play, Pause, Complete events
- Send data to GA4 or other platforms
Google Ads Conversion and Remarketing Tags in GTM
Conversion Tracking
- In Google Ads, create a conversion action
- Copy the Conversion ID and Label
- In GTM, use the Google Ads Conversion Tracking tag
- Add trigger (e.g., thank-you page view)
Remarketing Tag
- Use Google Ads Remarketing tag template
- Fire on All Pages
Debugging and Testing Your Tags
Before publishing changes:
- Use Preview mode to see if tags fire correctly
- Use Google Tag Assistant or GA4 DebugView
- Check real-time reports in GA4
Best Practices for Google Tag Manager
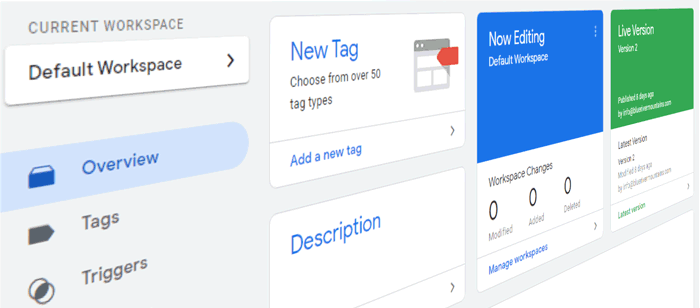
- Use workspaces for collaboration
- Name tags/triggers clearly for future reference
- Publish only after testing
- Use folders to organize tags
- Avoid redundant or conflicting tags
Common Errors and How to Fix Them
- Tags not firing? Check if triggers are configured correctly.
- Preview mode not working? Clear browser cache or use Incognito.
- Variables undefined? Enable them in Variables settings.
Advanced Features of Google Tag Manager
- Custom JavaScript variables
- Data Layer implementation for dynamic values
- Server-side tagging (for improved speed and privacy)
- Lookup tables and RegEx for complex logic
Wrapping Up: Why GTM Is a Game Changer for Marketers
Google Tag Manager empowers marketers and website owners to implement robust tracking without relying on developers for every change. Mastering GTM opens up deeper insights into user behavior, campaign performance, and business goals.
Whether you’re just starting out or looking to advance your tracking setup, GTM is an essential tool that will scale with your analytics needs.