What Is My IP Address? How It Works, How to Find and Protect It
Want to explore more about how IP addresses work or check your own IP location?
Visit our detailed guide here → IP Lookup
What Is My IP Address? A Complete Guide for Beginners and Tech Users
When you go online—whether to check your email, watch YouTube, or shop on Amazon—your device uses a unique digital identifier known as an IP address.

But what exactly is an IP address, how does it work, and why does it matter? Let’s break it down step by step.
What Is an IP Address?
An IP address (Internet Protocol address) is a unique number assigned to every device connected to the internet or a local network. It acts like your home address, but for your online presence—helping data find its way from one device to another.
When you send or receive data online, your IP ensures that information reaches the correct destination. Without IP addresses, the Internet simply couldn’t function.
How IP Addresses Work
Think of an IP like a digital return address. Whenever you connect to a website, your request travels through the internet, carrying your IP address with it. The server receiving your request uses that IP to know where to send the data back—just like mailing a letter and getting a reply.
Your Internet Service Provider (ISP) assigns your IP address each time you go online. This IP can be static (permanent) or dynamic (temporary and changes periodically).
The Two Main Types: IPv4 and IPv6
There are two primary versions of IP addresses used today: IPv4 and IPv6.
| Feature | IPv4 | IPv6 |
|---|---|---|
| Address format | 32-bit numeric (e.g., 192.168.1.1) | 128-bit alphanumeric (e.g., 2600:1512:5c3a::b762) |
| Total addresses | ~4.3 billion | Trillions (virtually unlimited) |
| Developed | 1980s | 1998 |
| Security | Relies on add-ons | Built-in IPsec encryption |
| Usage | Still widely used | Growing adoption globally |
IPv4 has been around since the early days of the Internet but is running out of available addresses.
IPv6 was developed to solve this limitation and to support the explosive growth of online devices—from smartphones to smart refrigerators.
Public vs Private IP Addresses
Public IP Address
A public IP address is the one assigned to your device by your ISP. It is visible to websites, online services, and anyone trying to identify your network.
- Used for: Internet communication
- Example: 203.0.113.45
- Visibility: Global (accessible over the Internet)
Your public IP helps websites know where to send content—like web pages or streaming video—to your device.
Private IP Address
A private IP address operates inside your home or office network. Devices like your phone, laptop, printer, and TV each have their own private IPs, which your router manages internally.
- Used for: Local communication within a network
- Example: 192.168.0.5
- Visibility: Hidden from the Internet
Private IPs can’t be accessed directly from the web; they sit safely behind your router or firewall.
Static vs Dynamic IP Addresses
Static IP addresses remain fixed, while dynamic IPs change periodically.
| Type | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Static | Manually assigned, stays the same | Businesses, servers, or VPN setups |
| Dynamic | Automatically assigned via DHCP | Home users, mobile devices |
Most users have dynamic IPs because they’re easier for ISPs to manage. However, a static IP can be useful for hosting websites, email servers, or remote access tools.
How to Find Your IP Address
There are two types of IPs you can check: public and private.
Step 1: Check Your Public IP Address
The fastest way:
Visit What is my ip address from WebFixGuide.com — your public IP address will appear automatically at the top of the page.
You can also simply search “What is my IP” on Google, and it will show your public IP address instantly.
Step 2: Find Your Private IP Address
Here’s how to locate your local IP depending on your device:
On Windows
+) Press Windows + R → type cmd → hit Enter
+) In the Command Prompt, type:
ipconfig+) Look for “IPv4 Address” under your network adapter.
On macOS
- Go to System Settings → Network → Wi-Fi → Details
- You’ll see your IPv4 or IPv6 address there.
On iPhone / iPad
Go to Settings → Wi-Fi → (i) next to your network → see “IP Address”.
On Android
Open Settings → Network & Internet → Wi-Fi → (your network) → look for “IP Address”.
Can Someone Find Me Through My IP Address?
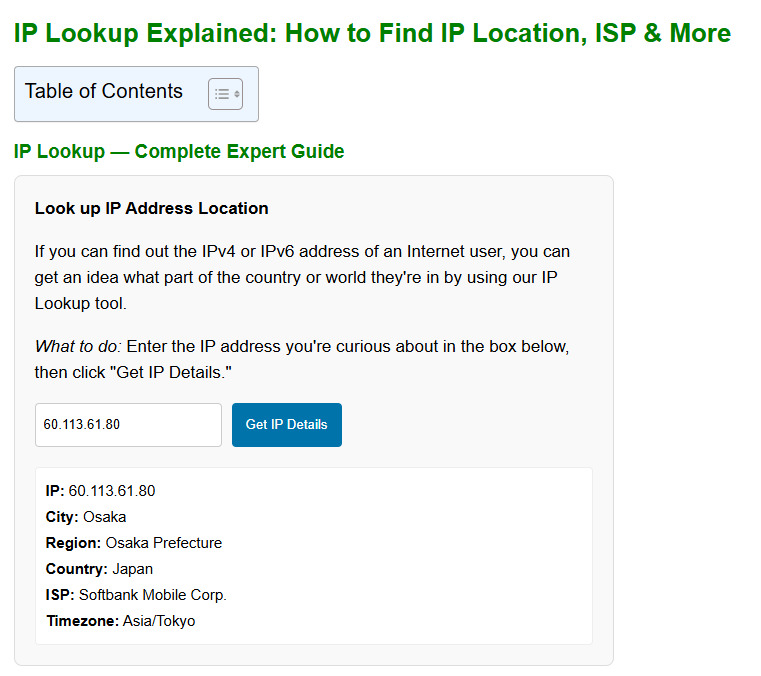
Your IP address can reveal your approximate location—such as your city or region—and the name of your Internet Service Provider (ISP).However, it cannot reveal your exact physical address or personal identity by itself.
That said, combining IP data with other tracking methods (like cookies or browser fingerprints) can increase privacy risks. That’s why many users choose to hide or change their IPs for better security.
How to Hide or Change Your IP Address
If you value online privacy or want to access region-restricted content, changing or masking your IP is a good idea.
Here are the most common methods:
Use a VPN (Virtual Private Network)
A VPN routes your internet traffic through an encrypted tunnel, hiding your real IP and replacing it with one from the VPN server.
Benefits include:
- Enhanced online privacy
- Access to geo-blocked content
- Protection on public Wi-Fi
Popular VPNs include NordVPN, ExpressVPN, CyberGhost, and Private Internet Access.
Use a Proxy Server
A proxy acts as an intermediary between your device and the websites you visit. It can change your visible IP address but doesn’t encrypt your traffic like a VPN.
Restart Your Router
Most ISPs assign dynamic IPs, meaning restarting your router can sometimes give you a new one.
Contact Your ISP
If you need a permanent change, ask your ISP to assign a new static IP.
Use the Tor Browser
Tor anonymizes your traffic by routing it through multiple nodes around the world, giving you a different IP each session.
Why Does My IP Address Change?
Your IP address may change because:
- You reconnect to your ISP or restart your router.
- You move to another location or network.
- Your ISP rotates dynamic IPs to manage users efficiently.
Frequent IP changes are completely normal and don’t usually affect performance.
Is It Safe to Share My IP Address?
In general, sharing your IP address publicly is not recommended. While it doesn’t directly expose sensitive data, it can make you a target for:
- Spam or phishing attempts
- DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks
- Basic geolocation tracking
For maximum safety, avoid posting your IP online and use security tools such as VPNs and firewalls.
Final Thoughts
Your IP address is your digital identity—it’s what connects your device to the internet and allows seamless communication between systems.
Knowing “What Is My IP Address” helps you understand how networks operate, enhances your online privacy, and empowers you to manage your digital security better.
If you’re curious about your current IP, its location, or type, visit WebFixGuide.com
You’ll instantly see your public IP address, along with tools and guides to check, change, and protect your online identity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is an IP address used for?
It identifies and locates your device on a network so data can be sent and received accurately.
Can my IP address reveal my exact location?
No. It only shows an approximate region or ISP information—not your exact address.
How often does my IP change?
Dynamic IPs can change every time your router reconnects or your ISP refreshes its network.
Is it legal to change my IP address?
Yes, it’s completely legal. Many users change their IPs for privacy, security, or content access reasons.
How do I protect my IP address from hackers?
Use a VPN, keep your firewall enabled, and avoid sharing your IP on public forums.